7 Powers is one of the seminal books in business strategy.
“Strategy” is the most abused word in business. Any new initiative is added with a suffix of “Strategy” to make it look important.This book does a great job of explaining what is strategy and what it is not and how to think about strategy for your business.
I rate this book a 5/5 for the crisp content and narrative. It is one of those books which will change how you think.

These are my book notes from the book –
What is Strategy?
The study of the fundamental determinants of potential business value. It can be defined as a combination of two factors
Strategy = Statics(Being there) + Dynamics(Getting there)
Statics is about “Staying at the top”. It is the study of how a business can differentiate itself from others using the various approaches.
Dynamics is all about “Getting to the top” . It is the study of the path to be taken to achieve the statics mentioned above.
What is Power?
Power is the set of conditions creating the potential for persistent differential returns
What is strategy?
The term “strategy” means the route to continuing Power in significant markets
Fundamental Equation of Strategy
NPV = M0 * g * s * m
M 0 ≡ current market size
g ≡ discounted market growth factor
s ≡ long-term market share
m ≡ long-term differential margin (net profit margin in excess of that needed to cover the cost of capital)
What are the 7 powers?
#1. Scale Economies
Definition – The quality of declining unit costs with the increasing scale of the business is referred to as Scale Economies
Why do Scale Economies lead to Power(potential for persistent differential returns)?
a. Benefit – Lowered Costs
b. Barrier – Prohibitive Costs of Share gains. For each attempt at share gain , price has to be paid by the competitor and it will be detrimental to their business.
c. Distribution Network Density –
As the density of a distribution network increases to accommodate more customers per area, delivery costs decline as more economical route structures can be accommodated.
eg – UPS, Amazon, Convoy are example of players who have leveraged their distribution network to reduce cost of incremental value delivered to the customers
d. Purchasing Economies – A large scale buyer can elicit better pricing for inputs
eg- Netflix in content streaming, Amazon in eCommerce
What must you do to get there?
You must simultaneously pursue a business model that promises Scale Economies (industry economics), while at the same time offering up a product differentially attractive enough to pull in customers and gain relative share (competitive position).
#2. Network Economies
Definition – Network Economies occur when the value of a product to a customer is increased by the use of the product by others.
Benefit – A company in a leadership position with Network Economies can charge higher prices than its competitors, because of the higher value as a result of more users.
Barrier – The barrier for Network Economies is the unattractive cost/benefit of gaining share, and this can be extremely high.
What must you do to get there?
The needs are similar to Scale Economies, except that installed base, rather than sales share, is the goal.
#3. Counter Positioning
Definition – A newcomer adopts a new, superior business model which the incumbent does not mimic due to anticipated damage to their existing business.
Benefit– The new business model is superior to the incumbent’s model due to lower costs and/or the ability to charge higher prices.
Barrier – Collateral Damage to the incumbent primary business model leads the incumbent to always choose the option of Staying the course vs reacting to what the upstart is doing. It is a calculated move and not that of ignorance/incompetence
What must you do to get there?
Examples – Dell vs. Compaq, Nokia vs. Apple, Amazon vs. Borders, In-N-Out vs. McDonalds, Charles Schwab vs. Merrill Lynch, Netflix vs. Blockbuster, etc. Nearly always, these featured the same outcome: the incumbent responds either not at all or too late.
#4. Switching Costs
Definition – The value loss expected by a customer that would be incurred from switching to an alternate supplier for additional purchases.
Benefit – A company that has embedded Switching Costs for its current customers can charge higher prices than competitors for equivalent products or services.
Barrier – To offer an equivalent product, competitors must compensate customers for Switching Costs.
Types of Switching Costs
- Financial
- Procedural
- Relational
#5. Branding
Definition – The value loss expected by a customer that would be incurred from switching to an alternate supplier for additional purchases.
Benefit – A business with Branding is able to charge a higher price for its offering due to affective valence(assumed benefits and association with the brand) and uncertainity reduction
Barrier – A strong brand can only be created over a lengthy period of reinforcing actions ( hysteresis ), which itself serves as the key Barrier.
#6. Cornered Resource
Definition – Preferential access at attractive terms to a coveted asset that can independently enhance value.
Benefit – The resource gives access to an uncommonly appealing product. It can be people, patents, movie deals etc. which can provide a continuous benefit to the business.
Barrier – The barrier can be general or personal. In case of Pixar, it was personal choice of the braintrust to continue working in Pixar versus joining some other company.
How to identify a cornered resource
- Idiosyncratic
- Non arbitraged
- Transferrable
- Ongoing
- Sufficient
What must you do to get there?
You must secure the rights to a valuable resource on attractive terms. This often comes from having developed that resource in the first place and then gaining ownership of it, the most common avenue being a patent award for research developments.
#7. Process Power
Definition – Embedded company organization and activity sets which enable lower costs and/or superior product, and which can be matched only by an extended commitment.
Benefit – A company with Process Power is able to improve product attributes and/or lower costs as a result of process improvements embedded within the organization.
Barrier – The Barrier in Process Power is hysteresis: these process advances are difficult to replicate, and can only be achieved over a long time period of sustained evolutionary advance.
Inherent speed limit in achieving this barrier is because of the following –
- Complexity
- Opacity – Instituion
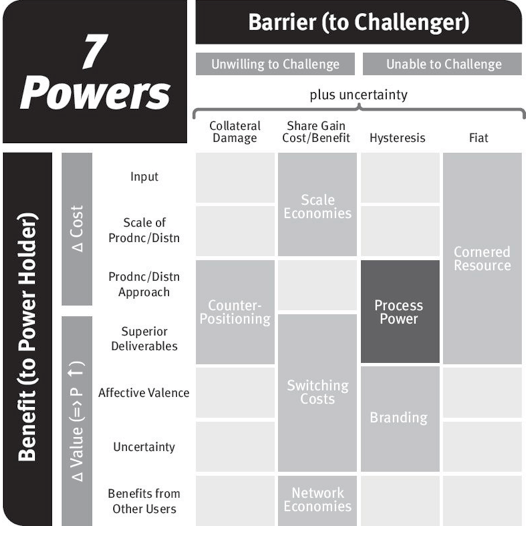
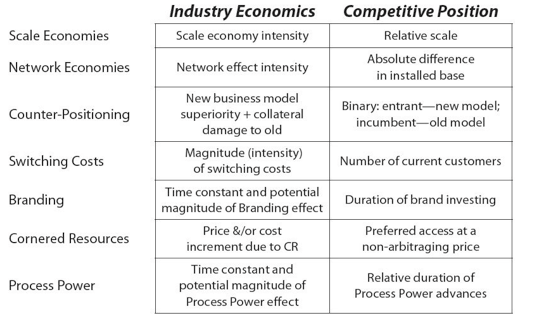
The Path to Power – What must I do ?
All power starts with invention.
There are three ways of value creation –
- Capabilities Led
- Customer Led
- Competitor Led
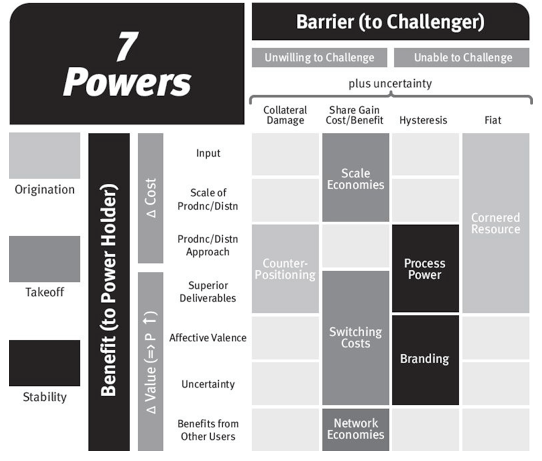
The Power Progression – When can I reach a position of Power?
- Origination – Cornered Resource and Counter Positioning
- Take Off – Scale Economies , Network Economies, Switching Costs
- Stability – Process Power , Branding
Additional Reading
If you are interested in learning more , these articles/videos will also help –
- https://stratechery.com/2019/netflix-flexes/
- https://stratechery.com/2015/netflix-and-the-conservation-of-attractive-profits/
- https://stratechery.com/2013/clayton-christensen-got-wrong/
Final Conclusion
Buy this book, it is worth it.